MatplotlibChartWithToolbar
Composite control that combines a MatplotlibChart with a ready-made toolbar UI.
Warning
This control requires the matplotlib
Python package to be installed.
See this installation guide for more information.
Inherits: Column
Properties
-
figure(Figure) –Matplotlib figure to draw - an instance of
Methods
-
download_click–Export the figure in the selected format and prompt user to save it.
-
on_message–Show status text produced by the underlying chart toolbar backend.
-
on_toolbar_update–Synchronize back/forward button enabled state with chart history.
-
pan_click–Toggle pan mode and ensure zoom mode is turned off.
-
zoom_click–Toggle zoom mode and ensure pan mode is turned off.
Examples#
Basic#
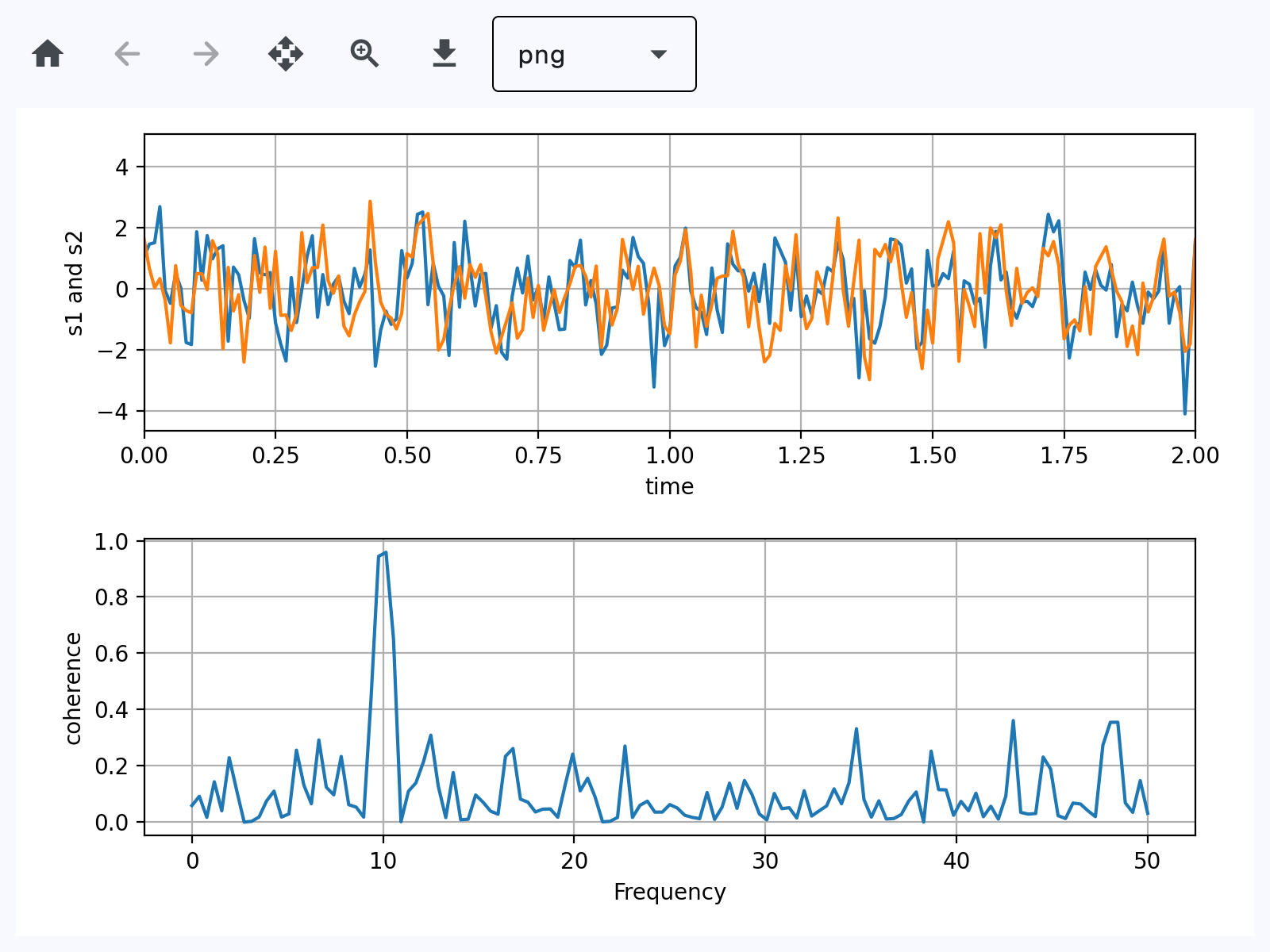
Based on an official Matplotlib example.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import flet as ft
import flet_charts as fch
def main(page: ft.Page):
# Fixing random state for reproducibility
np.random.seed(19680801)
dt = 0.01
t = np.arange(0, 30, dt)
nse1 = np.random.randn(len(t)) # white noise 1
nse2 = np.random.randn(len(t)) # white noise 2
# Two signals with a coherent part at 10Hz and a random part
s1 = np.sin(2 * np.pi * 10 * t) + nse1
s2 = np.sin(2 * np.pi * 10 * t) + nse2
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 1)
axs[0].plot(t, s1, t, s2)
axs[0].set_xlim(0, 2)
axs[0].set_xlabel("time")
axs[0].set_ylabel("s1 and s2")
axs[0].grid(True)
cxy, f = axs[1].cohere(s1, s2, 256, 1.0 / dt)
axs[1].set_ylabel("coherence")
fig.tight_layout()
page.add(fch.MatplotlibChartWithToolbar(figure=fig, expand=True))
if __name__ == "__main__":
ft.run(main)
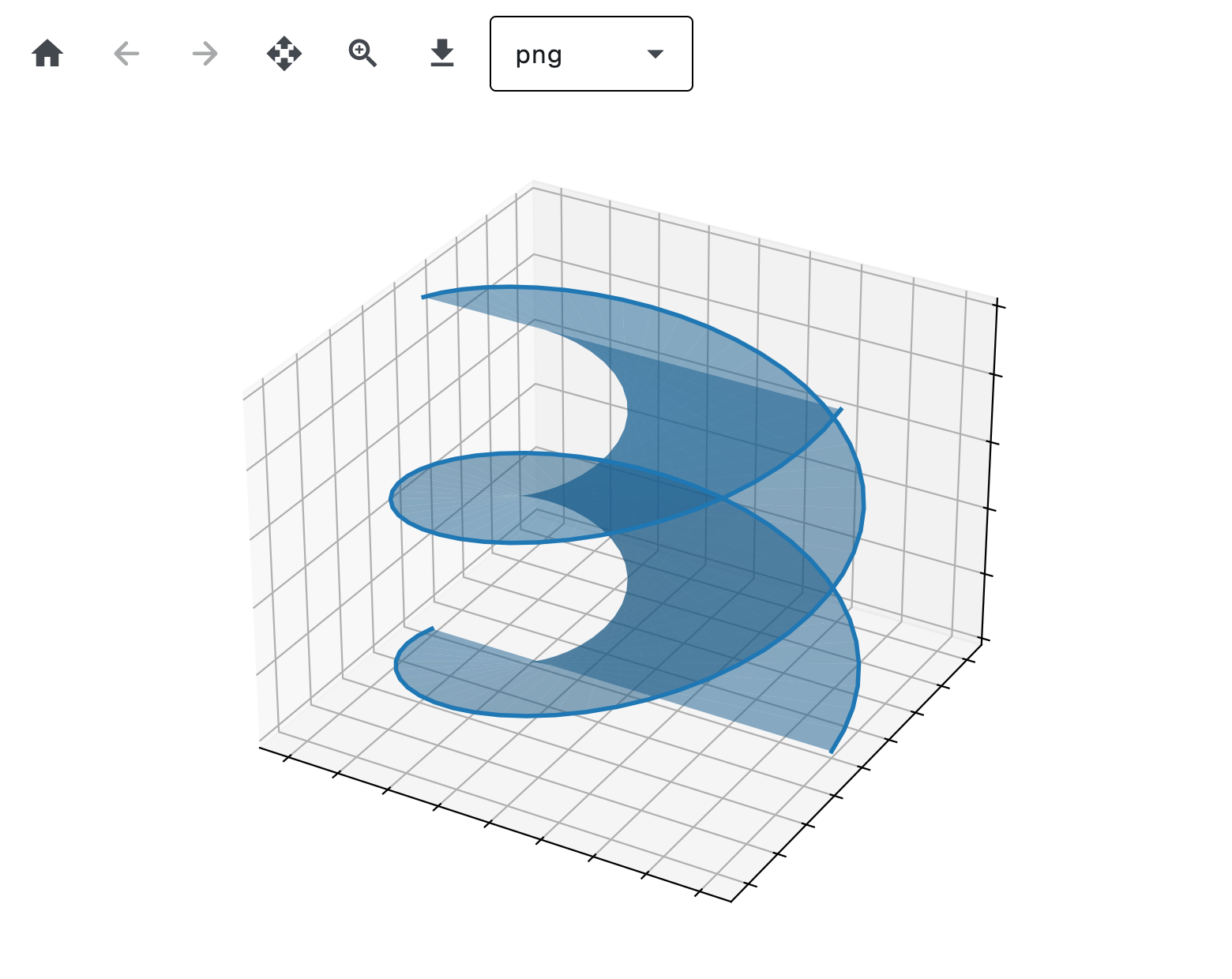
3D chart#
import logging
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import flet as ft
import flet_charts
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
def main(page: ft.Page):
plt.style.use("_mpl-gallery")
# Make data for a double helix
n = 50
theta = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, n)
x1 = np.cos(theta)
y1 = np.sin(theta)
z1 = np.linspace(0, 1, n)
x2 = np.cos(theta + np.pi)
y2 = np.sin(theta + np.pi)
z2 = z1
# Plot with defined figure size
fig, ax = plt.subplots(subplot_kw={"projection": "3d"}, figsize=(8, 6))
ax.fill_between(x1, y1, z1, x2, y2, z2, alpha=0.5)
ax.plot(x1, y1, z1, linewidth=2, color="C0")
ax.plot(x2, y2, z2, linewidth=2, color="C0")
ax.set(xticklabels=[], yticklabels=[], zticklabels=[])
page.add(flet_charts.MatplotlibChartWithToolbar(figure=fig))
if __name__ == "__main__":
ft.run(main)
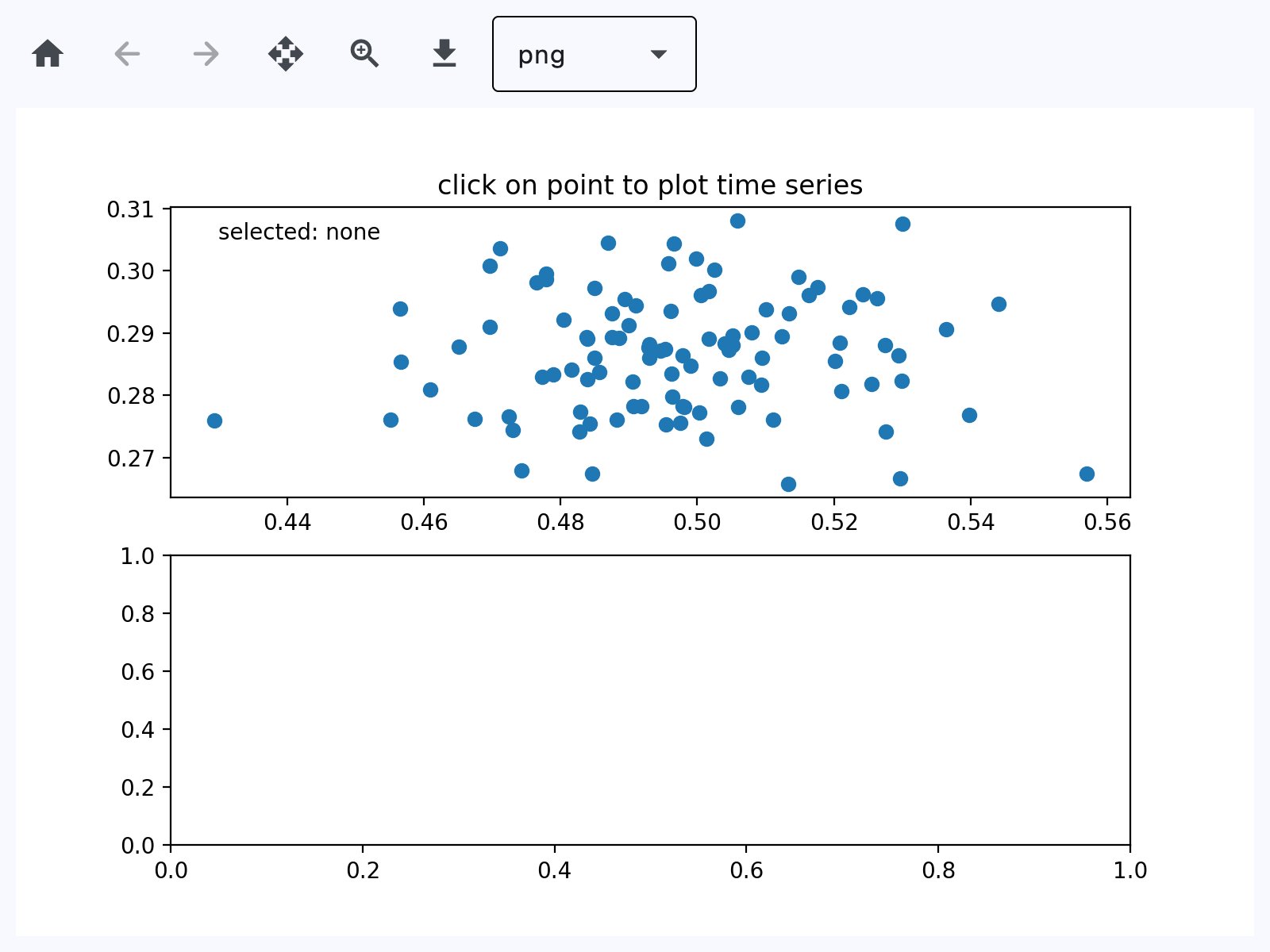
Handle events#
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import flet as ft
import flet_charts as fch
state = {}
def main(page: ft.Page):
# Fixing random state for reproducibility
np.random.seed(19680801)
X = np.random.rand(100, 200)
xs = np.mean(X, axis=1)
ys = np.std(X, axis=1)
fig, (ax, ax2) = plt.subplots(2, 1)
ax.set_title("click on point to plot time series")
(line,) = ax.plot(xs, ys, "o", picker=True, pickradius=5)
class PointBrowser:
"""
Click on a point to select and highlight it -- the data that
generated the point will be shown in the lower Axes. Use the 'n'
and 'p' keys to browse through the next and previous points
"""
def __init__(self):
self.lastind = 0
self.text = ax.text(
0.05, 0.95, "selected: none", transform=ax.transAxes, va="top"
)
(self.selected,) = ax.plot(
[xs[0]], [ys[0]], "o", ms=12, alpha=0.4, color="yellow", visible=False
)
def on_press(self, event):
if self.lastind is None:
return
if event.key not in ("n", "p"):
return
inc = 1 if event.key == "n" else -1
self.lastind += inc
self.lastind = np.clip(self.lastind, 0, len(xs) - 1)
self.update()
def on_pick(self, event):
if event.artist != line:
return True
N = len(event.ind)
if not N:
return True
# the click locations
x = event.mouseevent.xdata
y = event.mouseevent.ydata
distances = np.hypot(x - xs[event.ind], y - ys[event.ind])
indmin = distances.argmin()
dataind = event.ind[indmin]
self.lastind = dataind
self.update()
def update(self):
if self.lastind is None:
return
dataind = self.lastind
ax2.clear()
ax2.plot(X[dataind])
ax2.text(
0.05,
0.9,
f"mu={xs[dataind]:1.3f}\nsigma={ys[dataind]:1.3f}",
transform=ax2.transAxes,
va="top",
)
ax2.set_ylim(-0.5, 1.5)
self.selected.set_visible(True)
self.selected.set_data([xs[dataind]], [ys[dataind]])
self.text.set_text(f"selected: {dataind:d}")
fig.canvas.draw()
browser = PointBrowser()
state["browser"] = browser
fig.canvas.mpl_connect("pick_event", browser.on_pick)
fig.canvas.mpl_connect("key_press_event", browser.on_press)
# plt.show()
page.add(fch.MatplotlibChartWithToolbar(figure=fig, expand=True))
if __name__ == "__main__":
ft.run(main)
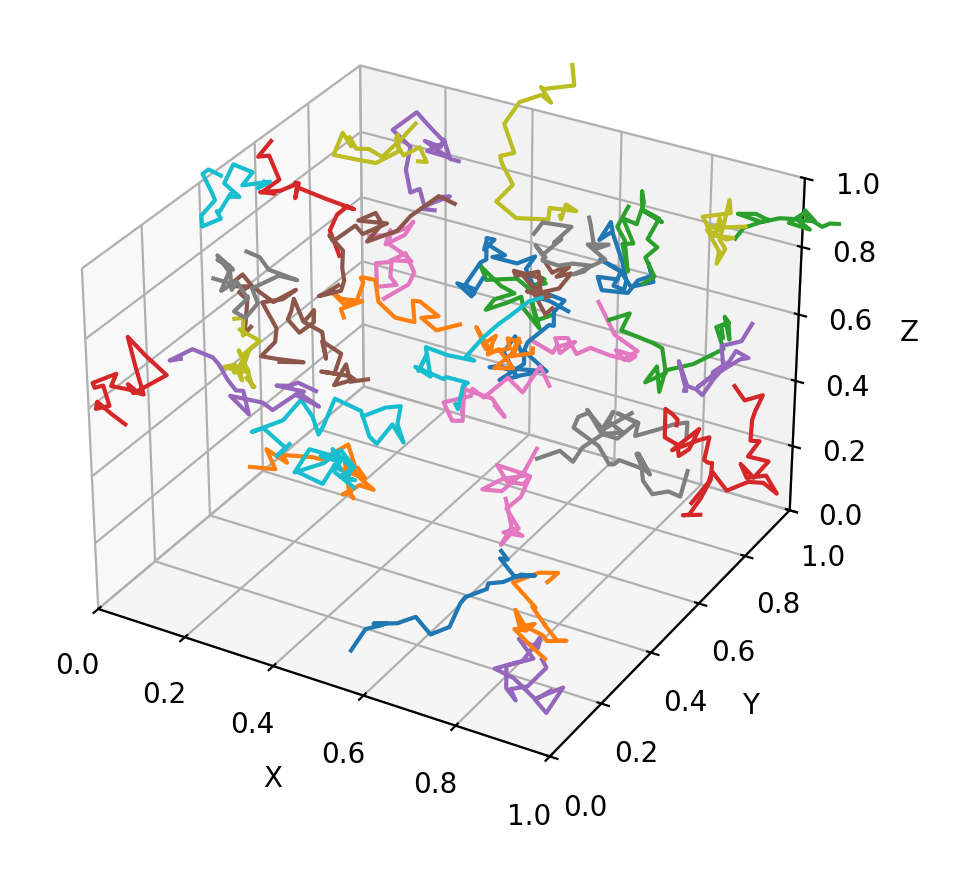
Animated chart#
import logging
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import flet as ft
import flet_charts
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
state = {}
def main(page: ft.Page):
import matplotlib.animation as animation
# Fixing random state for reproducibility
np.random.seed(19680801)
def random_walk(num_steps, max_step=0.05):
"""Return a 3D random walk as (num_steps, 3) array."""
start_pos = np.random.random(3)
steps = np.random.uniform(-max_step, max_step, size=(num_steps, 3))
walk = start_pos + np.cumsum(steps, axis=0)
return walk
def update_lines(num, walks, lines):
for line, walk in zip(lines, walks):
line.set_data_3d(walk[:num, :].T)
return lines
# Data: 40 random walks as (num_steps, 3) arrays
num_steps = 30
walks = [random_walk(num_steps) for index in range(40)]
# Attaching 3D axis to the figure
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(projection="3d")
# Create lines initially without data
lines = [ax.plot([], [], [])[0] for _ in walks]
# Setting the Axes properties
ax.set(xlim3d=(0, 1), xlabel="X")
ax.set(ylim3d=(0, 1), ylabel="Y")
ax.set(zlim3d=(0, 1), zlabel="Z")
# Creating the Animation object
state["anim"] = animation.FuncAnimation(
fig, update_lines, num_steps, fargs=(walks, lines), interval=100
)
page.add(flet_charts.MatplotlibChartWithToolbar(figure=fig, expand=True))
if __name__ == "__main__":
ft.run(main)
Properties#
class-attribute
instance-attribute
#
figure: Figure = field(metadata={'skip': True})
Matplotlib figure to draw - an instance of
matplotlib.figure.Figure.
Methods#
async
#
Export the figure in the selected format and prompt user to save it.
Show status text produced by the underlying chart toolbar backend.
Parameters:
-
e(MatplotlibChartMessageEvent) –Message event emitted by
MatplotlibChart.
Synchronize back/forward button enabled state with chart history.
Parameters:
-
e(MatplotlibChartToolbarButtonsUpdateEvent) –Toolbar state update event from
MatplotlibChart.